Thematic Project 1 氣膠對雲霧微物理性質及降水時空分布之影響
氣膠-雲-降水之交互作用在區域空氣品質、區域天氣與氣候研究中是最具挑戰性的科學議題之一。欲探討此一課題,需要對氣膠的形成、組成、傳輸以及它們的輻射、吸濕和微物理和化學特性有很好的瞭解,才能夠評估空間和時間尺度上對區域氣候、環境及水資源的可能衝擊。本整合計畫以”氣膠-雲霧-降雨”交互作用為研究主軸,探討氣膠物理化學特徵、形成機制及降雨的影響。研究包括三大部分: 第一部分為採樣觀測,包括5個子計畫: 研究重點包括氣膠生成機制及物理、化學及光學特徵,大氣液相物理、化學機制等。第二部分為遙測分析包括3計畫,主要利用光達量測氣膠分布及邊界層動力與局部環流之演變、衛星遙測探討空氣污染對雲/霧性質的影響以及瞭解低雲/霧發生的時空分布氣候特徵。氣象雷達了解降雨時空分布。第三部分也包括3個子計畫,以數值模擬為主,將探討台灣西部之空氣污染物傳輸與雲/霧滴物理化學特徵的關聯,邊界層發展及都市熱島效應與空氣污染物、氣膠間的交互作用傳輸的影響,同時也將探討氣膠如何抑制或增強降水,增進對空氣品質及水資源影響的評估能力。
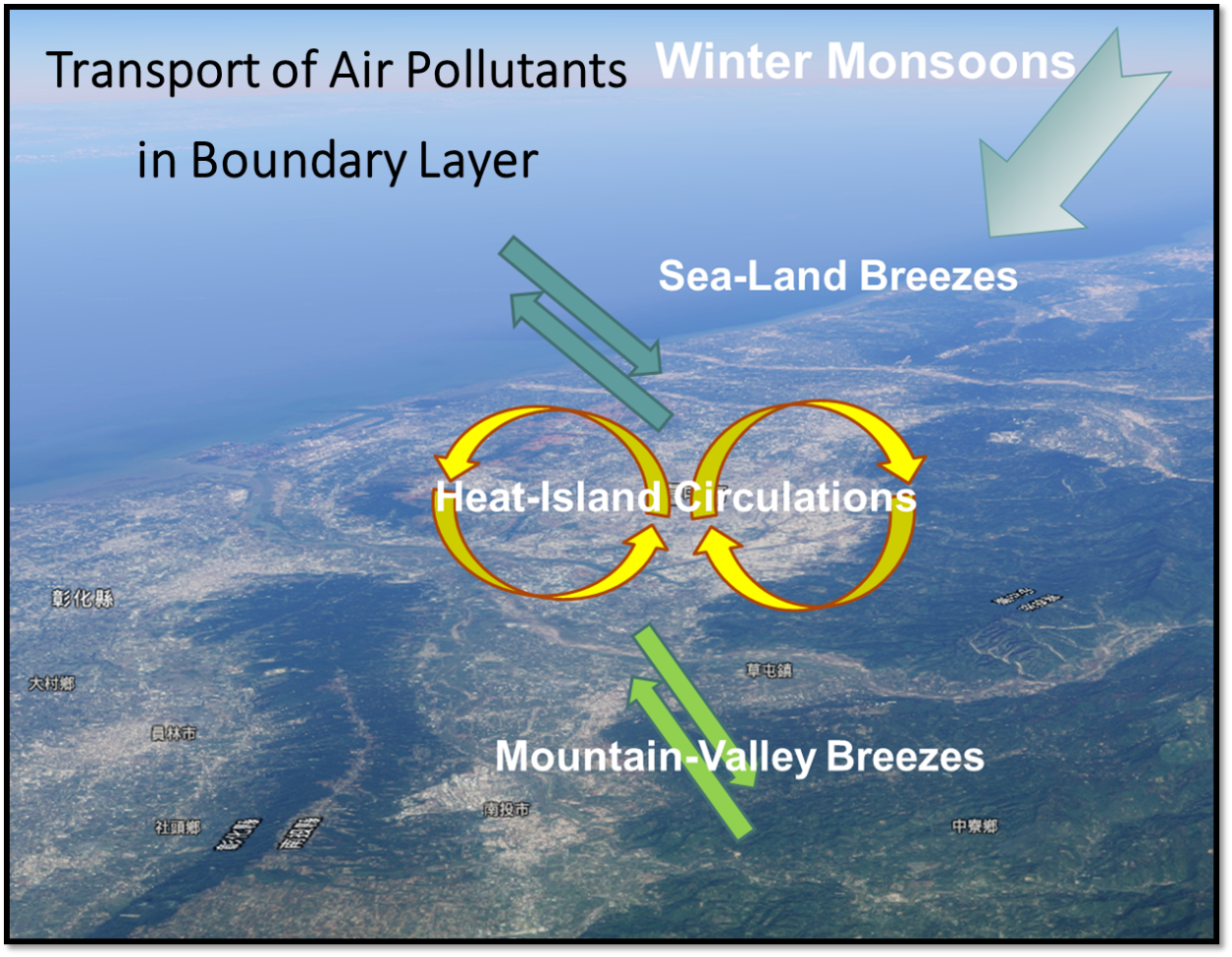
Thematic Project 2 Diagnosis and Attribution of Air Pollution in Central-Western Taiwan
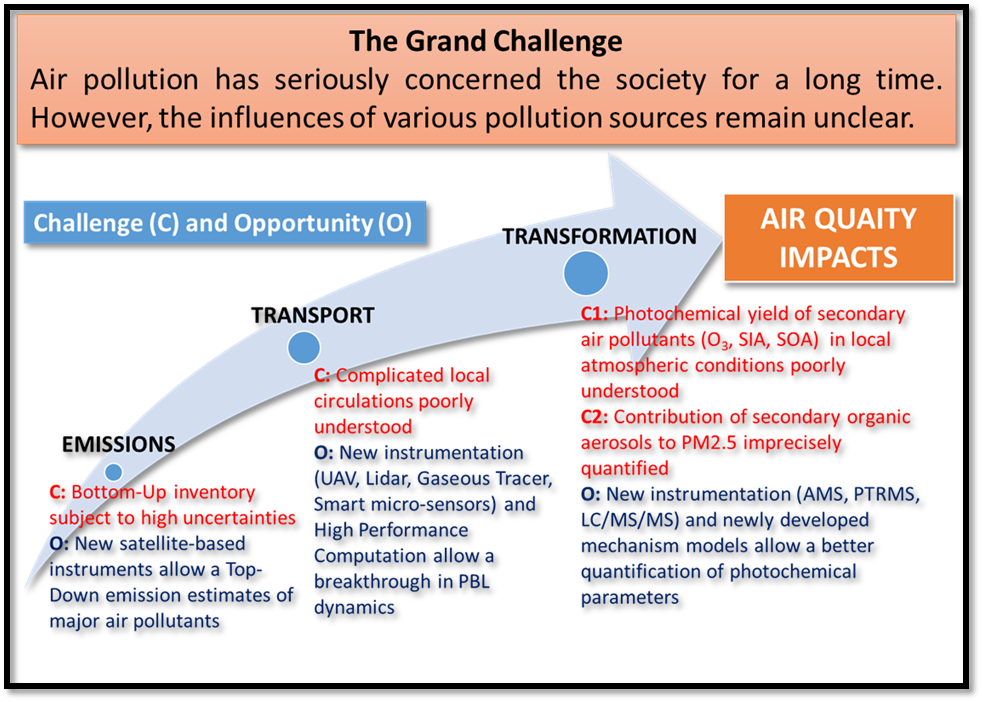
This is the flagship project of AQRC, which is supported by the Grand Challenge Program of Academia Sinica. We have identified some knowledge and/or technical issues that prevented us from formulation of an effective air pollution control strategy in Taiwan, which include uncertainties in emission inventory, poor understandings in local circulations and the photochemical production of secondary air pollutants. An integrated approach is proposed accordingly to investigate emissions, transport, and production/transformation of air pollutants. The data will support in-depth studies on the emission inventory, PBL structure and dynamics, and production of secondary air pollutants (O3 and PM2.5). The outcomes of this study will contribute crucial data and knowledge to the formulation of effective mitigation strategies of air pollution in the Central-Western Taiwan. Furthermore, the outcomes of this study will stimulate knowledge fusion among traditional PBL meteorology, atmospheric chemistry, and space sciences, which could in turn provide new perspectives in urban planning.
Thematic Project 3 Development of High-Resolution Air Quality Forecast and Diagnosis Model
This is a representative project that bridges our scientific capability to the needs of the society. In order to improve the air quality forecast service in Taiwan, the Ministry of Science and Technology launched a mission-oriented program in 2017. The RCEC team is assigned to be in charge of developing an air quality forecast/diagnosis system, which is based on atmospheric chemistry and transport models and thereby is able to simulate and reproduce the sophisticated processes for air quality deterioration. During the last four years, the outcomes of this project have significantly improved the operational forecast of Air Quality Index over Taiwan. In the next 4 years, our on-going tasks aim at further improvement in the spatial resolution of air quality forecast and development of tools for management of urban air quality.
Thematic Project 4 Effect of Megacities on the Transport and Transformation of Pollutants on the Regional and Global Scales - Asia (EMeRGe-Asia)
Urban air pollution is among the common issues faced by both the developing and developed countries. Due to the rapid industrialization in the last 20 years, the East Asia (particularly China) has become one of the major source regions of air pollutants in the world. The EMeRGe is an international project funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) and led by the scientists of the University Bremen . The East Asia is one of the major study areas of this project and thereby a local research group is essential to the research project. RCEC has participated the EMeRGe as an international member since the planning phase of the EMeRGe in Asia. Finally, the EMeRGe-Asia had had Taiwan as the local base and a high precision atmospheric chemistry experiment was performed in the spring of 2018. The Germany group conducted 10 research flight missions on the HALO research aircraft in the EA continental outflow regions, and RCEC scientists conducted complementary ground-based investigations of air pollutants and planetary boundary layer dynamics, as well as forecast of the continental pollution outbreaks and the transport path, which was essential to the planning of research flight missions. The outcomes of this study will contribute to not only the scientific understandings of the atmospheric composition and processes but also the assessment of the influences of regional air pollution to the local air quality in Taiwan. Moreover, this project has setup a strong linkage between the Taiwan and Germany research communities. Further Taiwan-Germany collaboration on the atmospheric sciences are expected in the future.
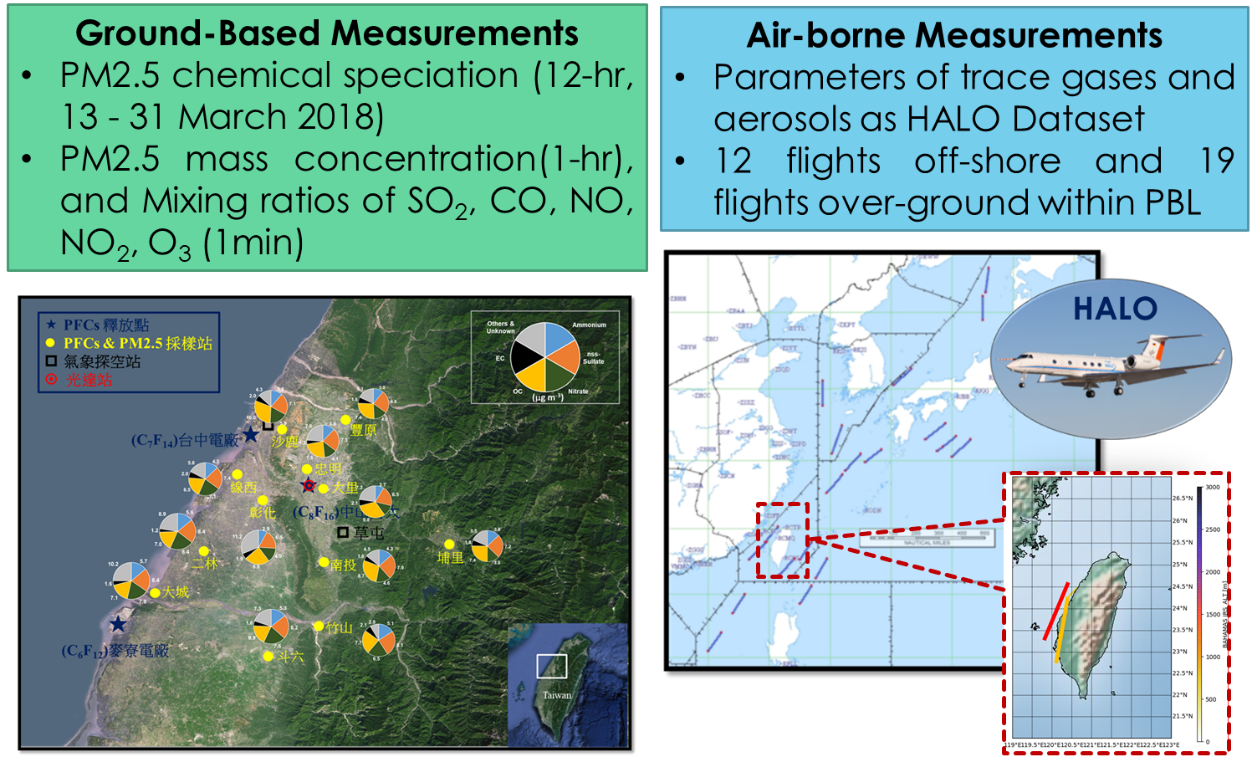
Thematic Project 5 Formation and Transport of Air Pollutants around Megacities in Taiwan
The aim of this project is to improve our understandings on the formation and transport of urban air pollutants in Taiwan and, in turn, the relevant impacts upon the environment in the outskirt areas of a megacity. During the last 5 years, a series of observation and simulation experiments were conducted in the western Taiwan, where a vast amount of air pollutants was emitted. The results of this study revealed that photochemical oxidation of SO2/NOx/VOCs was responsible most for the high PM2.5 levels over the western Taiwan. Furthermore, it was found that the local circulations like sea breezes and the orographic winds transported the urban air pollutants into the forested areas on the western slope of the Central Mountain Range of Taiwan, which then interacted chemically with biogenic VOCs and resulted in production of biogenic secondary aerosols. The intrusion of urban air pollution could have caused changes in the amount and hygroscopic properties of aerosols over the mountainous areas in Taiwan.